Currently Empty: €0.00
Calcium Phosphate Monohydrate (CAS 7758-23-8)
Calcium Phosphate Monohydrate (CAS 7758-23-8)
Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 (“AMCP” or “CMP-A” for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate (“MCP” or “MCP-M”), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless solids. They are used mainly as superphosphate fertilizers and are also popular leavening agents.
Other names
Acid calcium phosphate
Calcium acid phosphate
Calcium diorthophosphate
Calcium biphosphate
Calcium superphosphate
Monobasic calcium phosphate
Monocalcium orthophosphate
Phosphoric acid, calcium salt (2:1)
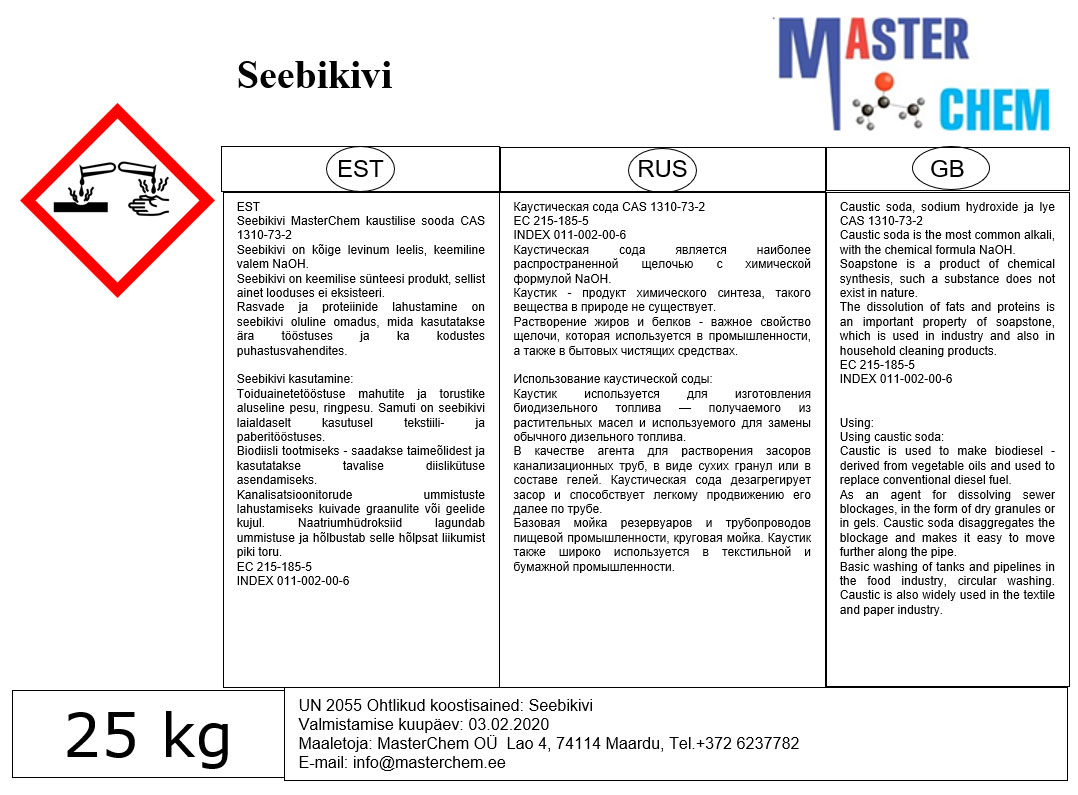
Caustic soda (CAS 1310-73-2)
Caustic soda, sodium hydroxide ja lye CAS 1310-73-2
Caustic soda is the most common alkali, with the chemical formula NaOH.
Soapstone is a product of chemical synthesis, such a substance does not exist in nature.
The dissolution of fats and proteins is an important property of soapstone, which is used in industry and also in household cleaning products.
EC 215-185-5
INDEX 011-002-00-6
Cholesterol (CAS 57-88-5)
Cholesterol (CAS 57-88-5)
Cholesterol (from the Ancient Greek chole- (bile) and stereos (solid), followed by the chemical suffix -ol for an alcohol) is an organic molecule. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. It is a yellowish crystalline solid.
Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as Mycoplasma, which require cholesterol for growth.
François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound “cholesterine”.
Cobalt chloride (CAS 7646-79-9)
Manganese chloride tetrahydrate (CAS 13446-34-9)
Cobalt(II) chloride is an inorganic compound of cobalt and chlorine, with the formula CoCl2. It is a red crystalline solid.
Because of the ease of the hydration/dehydration reaction, and the resulting color change, cobalt chloride is used as an indicator for water in desiccants.
Niche uses of cobalt chloride include its role in organic synthesis and electroplating objects with cobalt metal.
Cobalt chloride has been classified as a substance of very high concern by the European Chemicals Agency as it is a suspected carcinogen.
Copper chelate EDTA 15% (CAS 14025-15-1)
Copper chelate EDTA 15% (CAS 14025-15-1)
Copper chelate EDTA 15% is a chelated single micronutrient fertilizer of high purity. Thanks to its unique patented raspberry-shaped microgranule, it is dust free, easy flowing and it dissolves rapidly. It is recommended to cure Copper deficiency on all crops.
– Suitable for organic farming in compliance with European Regulation (EU) 2018/848
– Cures Copper deficiency – shown as curled – small new leaves
– Copper 100% chelated and fully available up to a pH of 9
– Developed for foliar application. Also suitable for fertigation in open field and greenhouses
– Soft for leaf tissue
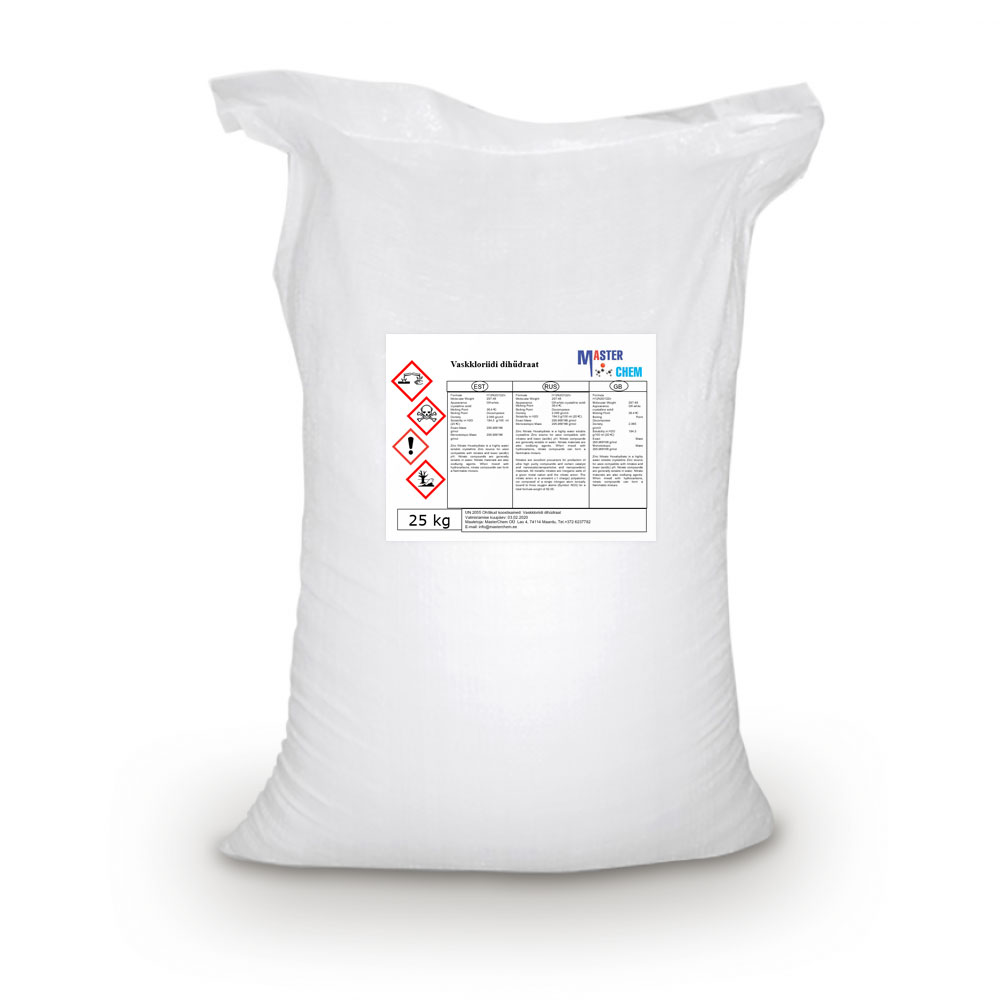
Copper chloride dihydrate (CAS 10125-13-0)
Copper chloride dihydrate (CAS 10125-13-0)
Copper(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The anhydrous form is yellowish brown but slowly absorbs moisture to form a blue-green dihydrate.
Both the anhydrous and the dihydrate forms occur naturally as the very rare minerals tolbachite and eriochalcite, respectively.
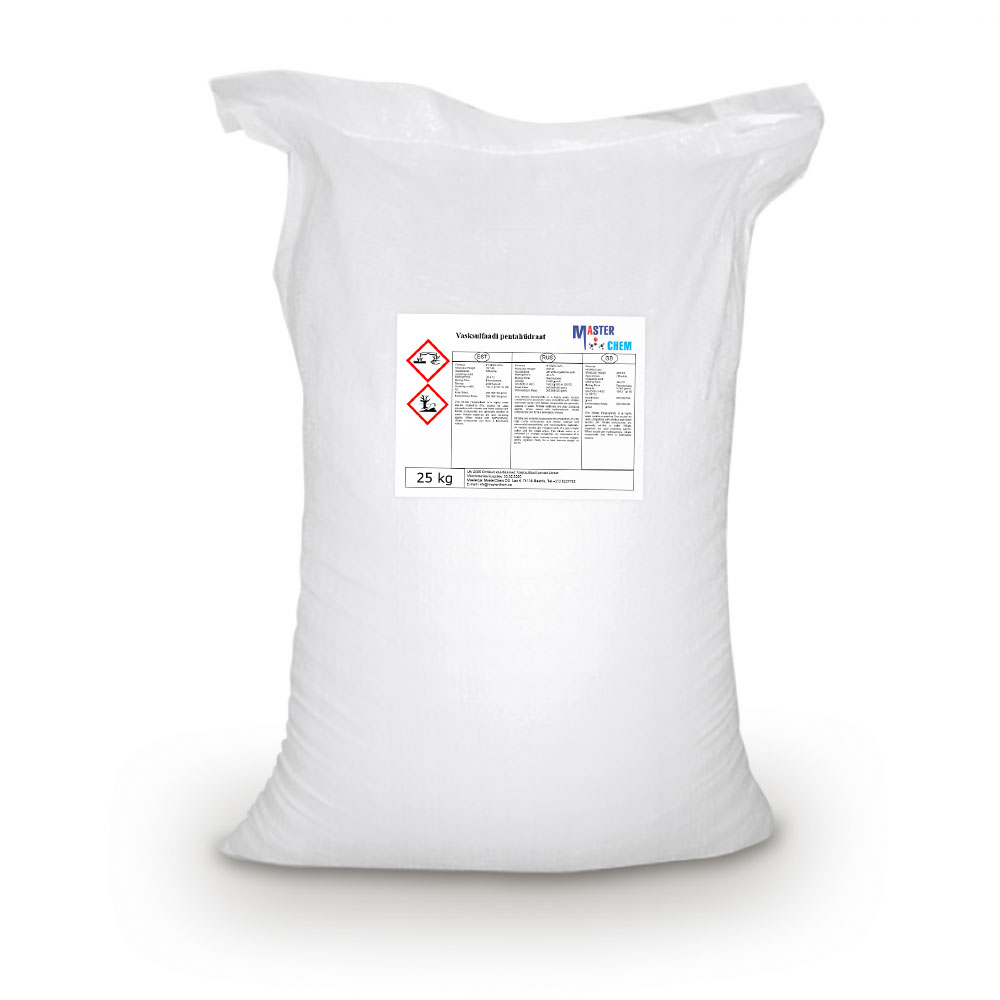
Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate (CAS 7758-99-8)
Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate (CAS 7758-99-8)
Copper(II) sulfate, also known as copper sulphate, are the inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CuSO4(H2O)x, where x can range from 0 to 5. The pentahydrate (x = 5) is the most common form. Older names for this compound include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol.
The pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O), the most commonly encountered salt, is bright blue. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains. Anhydrous copper sulfate is a light grey powder.
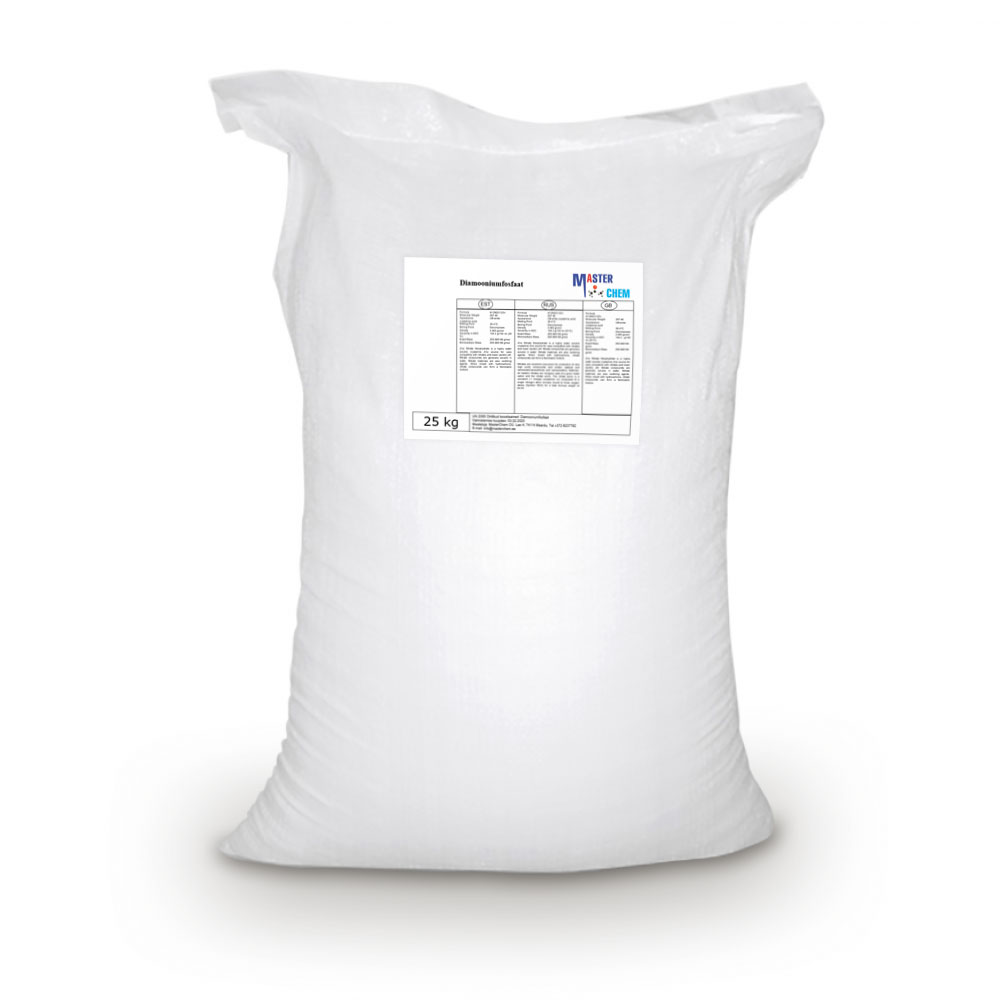
Diammonium Phosphate (CAS 7783-28-0)
Diammonium Phosphate (CAS 7783-28-0)
Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4) is one of a series of water-soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid.
According to the diammonium phosphate MSDS from CF Industries, Inc., decomposition starts as low as 70 °C: “Hazardous Decomposition Products: Gradually loses ammonia when exposed to air at room temperature. Decomposes to ammonia and monoammonium phosphate at around 70 °C (158 °F). At 155 °C (311 °F), DAP emits phosphorus oxides, nitrogen oxides and ammonia.”
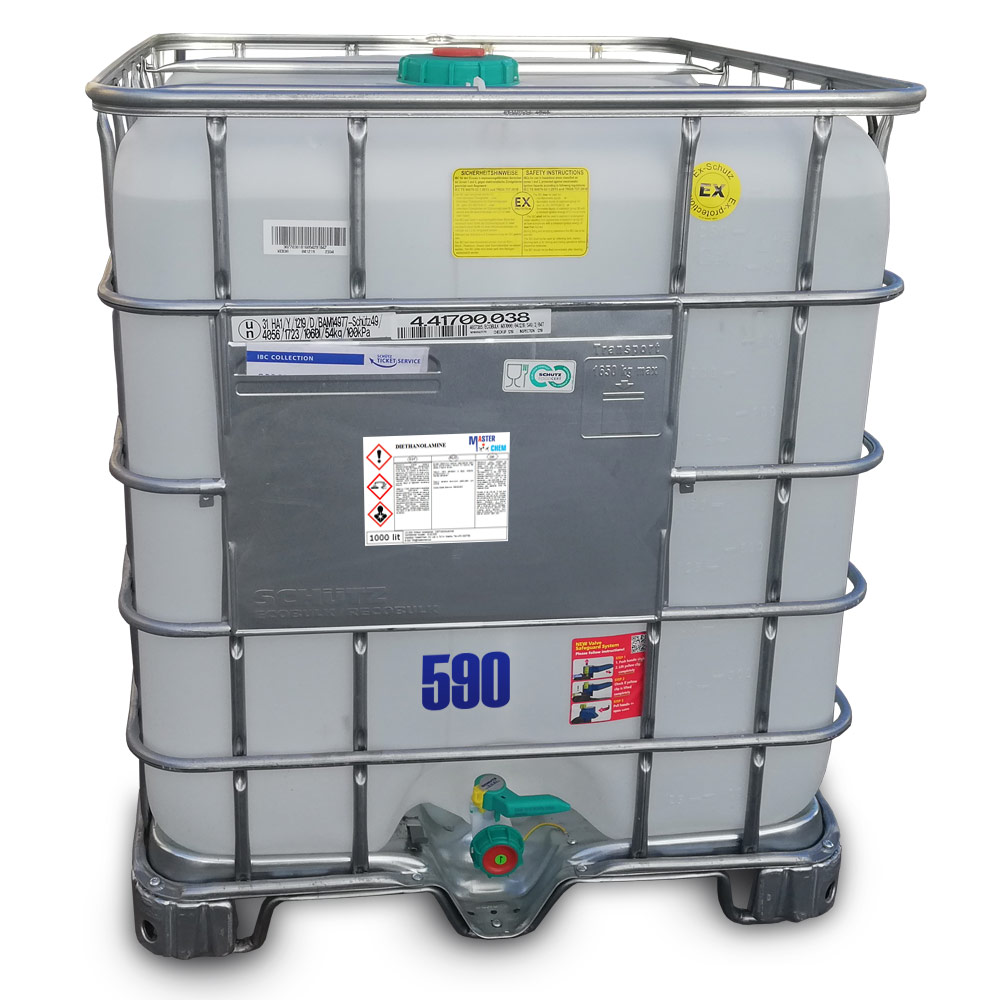
Diethanolamine (CAS 111-42-2)
Other names: Bis(hydroxyethyl)amine, N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amine, 2,2′-Dihydroxydiethylamine, β,β’-Dihydroxydiethylamine, Diolamine, 2-[(2-Hydroxyethyl)amino]ethanol, 2,2′-Iminobisethanol, Iminodiethanol, Di(2-hydroxyethyl)amine, bis(2-Hydroxyethyl)amine, 2,2′-Iminodiethanol
DEA is used as a surfactant and a corrosion inhibitor. It is used to remove hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide from natural gas.
In oil refineries, a DEA in water solution is commonly used to remove hydrogen sulfide from sour gas. It has an advantage over a similar amine ethanolamine in that a higher concentration may be used for the same corrosion potential. This allows refiners to scrub hydrogen sulfide at a lower circulating amine rate with less overall energy usage.
DEA is a chemical feedstock used in the production of morpholine.
CAS 111-42-2
Disodium octaborate tetrahydrate (CAS 12280-03-4)
Disodium octaborate tetrahydrate (CAS 12280-03-4)
Disodium octaborate tetrahydrate, an alkaline salt, is produced in two forms. One is a clear, liquid concentrate or it is packaged as a white, odorless, powdered chemical substance that is not flammable, combustible, or explosive and has low acute oral and dermal toxicity. This salt, which is commonly confused with boric acid, is used as an insecticide and is commonly sold in liquid or powder form. It is also effective against fungi and algae. It has an unlimited shelf life and is not affected by temperature.
This chemical is also a flame-retardant. In the liquid form, it is commonly diluted and sprayed on wood surfaces to kill termites, powder post beetles, carpenter ants, fungi and algae. It is also available as pellets for embedding in structural wood. This alkaline salt is not to be confused with boric acid (an acidic chemical) or the laundry detergent additive used for stains.
In common use as a termite control or for termite prevention, the liquid concentrate is used at a ratio of 1:1 with water. The advantages to this chemical over conventional pest control treatment is that it is non-carcinogenic and has a low toxicity to humans and pets. It is also odorless and proper application lasts for the lifetime of the wood. Repeat treatment is not necessary. It is best used during new construction, however, it is more commonly used after the fact on homes originally treated with chemicals that have become inactive.
Ethanolamine (CAS 141-43-5)
Ethanolamine (CAS 141-43-5)
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is an organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH2NH2 (C2H7NO). The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid with an odor reminiscent of ammonia. Its derivatives are widespread in nature; e.g., lipids, as precursor of a variety of N-acylethanolamines (NAEs), that modulate several animal and plant physiological processes such as seed germination, plant–pathogen interactions, chloroplast development and flowering, as well as precursor, combined with arachidonic acid (C20H32O2; 20:4, ω-6), to form the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA: C22H37NO2; 20:4, ω-6).
The ethanolamines comprise a group of amino alcohols. A class of antihistamines is identified as ethanolamines, which includes carbinoxamine, clemastine, dimenhydrinate, Chlorphenoxamine, diphenhydramine and doxylamine.
Ethylene glycol (CAS 107-21-1)
Ethylene glycol (1,2-dioxane, glycol, ethanediol-1,2) is a sweet-tasting, odorless, colorless, hygroscopic oily liquid. It is obtained by wetting ethylene in the presence of phosphoric or sulfuric acids. Ethylene glycol mixes well with water and alcohol. It has high boiling points and low freezing temperatures, which is why it is widely used as a heat carrier in heating and cooling systems. The crystallization temperature of the concentrate is higher than that of aqueous glycol solutions, therefore it must be diluted with distilled water before use.
CAS: 107-21-1
- Ethylene glycol 35%
- Ethylene glycol 40%
- Ethylene glycol 50%
- Ethylene glycol 100%